- Home
- Education in India
Education in India
Updated on 27-03-2020
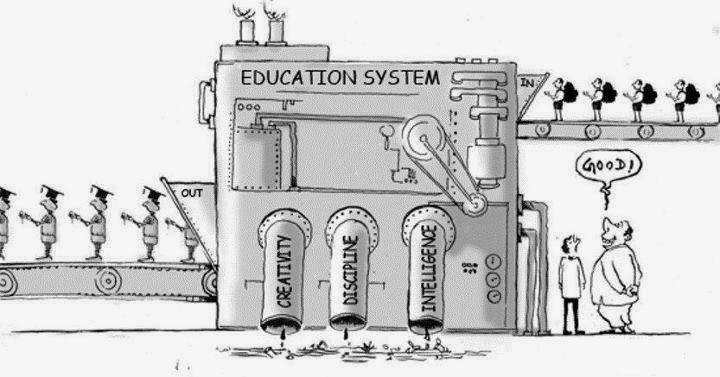
Education in India. Education is an important feature of life. ‘Literacy rate’ is a common measure used to measure and compare how educated are citizens in a country or a state or city. India’s literacy rate was at appalling 12% in 1947 when India got its Independence.
India has made significant progress in the field of education over the last few decades and the current literacy rate stands at 74% with many states attaining more than 90% literacy rate. This progress was made possible through many schemes of Govt specifically targeting the kids in rural areas and economically weaker sections through schemes such as mid day meal, free education up to class 7 (up to age of 12), no detention till class 8 (up to age 13) etc.
One of the important features of Indian education system is ‘reservations’. Reservation is based on physical ability, economic status, caste etc. Certain percent of seats are reserved for the above sections in all educational institutes. Also the fee for the reserved categories is discounted.
Reservations are a very popular political
means to attract votes and there is always immense pressure to add more castes/
creeds into these reserved categories.
Sensing the danger, Supreme Court of India has capped that reservations
cannot exceed 50% in aggregate
History of education in India
India is considered as one of the ancient and
culturally rich country. It is believed that during the early period education
was taught orally by the sages to their disciples. This way it was passed
orally from one generation to another generation for many years.
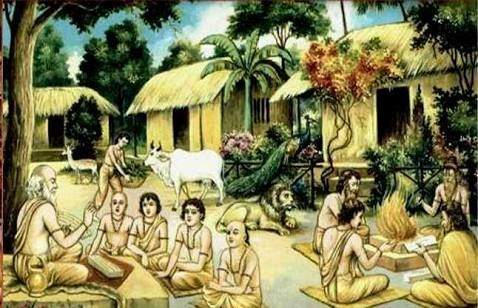
Later as there was overall progression the system in the education also further developed. In ancient times a very interesting system of education came up which was known as Gurukula. It is basically a Sanskrit word which means Guru means teacher and kula means home. In this system of Gurukula both teacher and the student stayed in the same house.
The main purpose of this system was to that students not only got education from the texts but also understood the day to day activities which were very essential for developing self discipline among the students. After completing their education Shishya or the disciple gave gurudakshina to guru. Gurudakshina means a small token of respect given to the guru in the form of monetary or in any other form. It is showing respect and gratitude to the Guru.
The main source of ancient education was Vedic literature. During the Vedic period usually forest was the place for teaching. The system of education during Vedic period was completely different from the present day system of education. In Vedic literature the disciples were given education on four different Vedas, Four Upavedas, Bhagavad-Gita and three smritis. As the student would stay in the house of Guru, he was considered as parent, philosopher and also evaluator.
The most important duty and objective
of the ancient education system was preserve and transmit the ancient Indian
rich culture. It was orally transmitted from guru to Shishya. During this
period Guru tried to develop the over all personality of student which included
physical, mental and developing good character among the students. Another
objective was inculcation of social and civic duties which were required for a
better future life after going out from the gurukul.
During the ancient period education was also
imparted based on the caste of the disciple. Brahmin was made to learn all the
Vedas, scriptures and religion, Kshatriya was given education about the skills
of warfare, Vaishyas learnt about commerce and Shudras who were men of working
class were given education based on different skills.
Levels of Education in India
Like many countries, In India the education system is divided into public and private. The funding or grants for each sector depends on central, state and the local bodies. The fee in public schools is generally lower than private schools. The quality of education also differs from public to private schools. In India both central and state boards follow the pattern of 10 + 2 + 3 pattern of education.
Indian education has different levels according to the age. Children start their schooling around 3years with pre-Nursery. Further the Pre Primary education is divided into Play group (2-3 years of age). Then Nursery age group is from 3-4 years. The concept behind these two group is that the child would get adjusted with the school environment.
Then
comes the L.K.G or Lower kindergarten with age group of 4-5 years and Upper
Kindergarten or U.K.G age group of 5-6 years. A systematic system of education
is followed in the early years of Children education mainly to build confidence
and make the child emotionally and mentally strong.
Pre- Primary - It consists of the age group of 3-5 years. The main aim of this level is to make children to come out of home and enjoy the beginning of education. It is divided into nursery, lower kindergarten (LKG) and upper kindergarten (UKG). At this stage kids are taught to know the basic alphabets and some reading.
Primary - It includes the age group of children of 6-11 years studying in classes from first to fifth. By the time children come to this stage they would have started accustomed to the school and would have some knowledge of alphabets and few sentences. Children would also be interested in learning maths and different body parts of human beings. The Indian government lays emphasis on the primary education. It lays foundation for further higher studies. Government has announced that no child should be detained in primary education.
Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan is an initiative by
government of India for achievement of Universalization of Elementary
education. The programme was started by Late former Indian Prime Minister Shri
Atal Bihari Vajpayee. The purpose of this programme was to provide compulsory
education for children of 6-14 years age group. Further to keep a track of the
programme the government of India launched a portal called as Shagun
Middle – It includes
the age group of children of 12-14 years studying in classes from 6 to 8. As
one climbs the ladder the system of education also become tougher and
interesting. Regular exams are conducted to know the development of each child.
Based on his/ her performance grades are given and lesser grade child would be
given special attention to improve his grades. This age group of
education sets a good base in Maths and science for higher education.
Secondary – It includes the age group of children of 15-16years studying in class 9 and 10. With adolescent creeping in the burden of studies also increases. The career of the child depends on how well he/she bears the pressure and handles it with confidence. In class 9, science is further divided into physics, chemistry and Biology. Maths becomes in depth in arithmetic, algebra and geometry. These two years are crucial to decide the path in which a student’s decide to choose his career. It can be science, commerce or arts.
Higher Secondary - It includes students studying in class 11 and 12. In state board run
schools it is called as PUC after 10th. Students choose the stream after
completing class 10. Based on the percentage scored in class 10 and interest of
the student they can choose Commerce, Science, Arts in class 11 or PUC. A
commerce student usually takes the stream of charted accountant or company
sectary. Science students can choose either medical or engineering depending
upon the subjects opted in class 11 and 12. The student who has chosen biology
can choose for engineering or medical.
Graduate - Here, a student goes through higher education, which is completed in college. This course may vary according to the subject pursued by the student. For medical student this stage is of four and a half years plus one year of compulsory internship, while a simple graduate degree can be attained in three years. Engineering takes four years while a law graduate studies for 5years.
Postgraduate - After completing graduation a student may opt for post graduation to
further add to his qualifications. Depending upon stream taken a student
decides to further add cap in his field to improve his career.
The pattern of examination up to 10th is same all over India in Central board. Students are graded based on his/her performance throughout the year in school. Marks are divided so that the children doesn’t have to bear the pressure. Marks are awarded for the behaviour of the child in the class.
The grading system includes A1, A2, b1 and 2 and further. Students who scores between 91-100 is considered as A1 grade in that particular subject. From 81-100 it is considered as A2 grade and the same way from 71-80 is considered as B1 and 61-70 it is considered as B2. Students who score less than B grade are given special attention and are given extra classes to improve their grades.
The first 10 year is further divided into two parts viz primary school (first seven year, class 1 to 7) high school (last 3years, class 8 to 10)
Curriculum and Boards of education in India
The first 10 year is further divided into two parts viz primary school (first seven year, class 1 to 7) high school (last 3years, class 8 to 10)
In India schools offer both Indian and international syllabi. There are different boards/ institutes responsible for the schooling as below:
- CBSE: Central Board of Secondary Education
- State Board: State Government Recognized Board.
- IGCSE: International General Certificate of Secondary Education, Cambridge University
- CISCE: Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations
- IB: International Baccalaureate
CBSE is the most preferred board by parents with transferable jobs, which was set up in 1962. The pattern of education in India from class 1 till 10 is continuous comprehensive education. System of marks was discontinued recently and a grading system was introduced to reduce the stress on children. CBSE conducts exams for class 10 and class 12 only and for rest of the classes the exams are conducted by the schools themselves.
This curriculum is most suited for the kids who have potential chances of moving from one state in India to another state in India due to the movement of their parents as the curriculum presents national perspective. All schools through out India that follow this curriculum are governed from Delhi.
State Board
Each state have their own board recognised by the Indian Government. The exams are conducted at primary, secondary and at higher levels. Board exams are conducted for class 10 and class 12 (which is called as 2nd PUC – pre university college). This curriculum is most suited for the kids who are not expected to move out of their state in India to another state in India due to the job (mostly in state govt jobs) or occupation (in business) of their parents. All schools that follow this curriculum are governed from the capital of each state in India.
CISCE
Council for the Indian School certificate examinations was set up in the year 1958. CISCE is a private nongovernmental organisations that conducts examination of Indian Certificate of Secondary Education(ICSE), The Indian School Certificate (ISC) for class 10 and 12 respectively. Even they conduct board exams for class 10 and 12.
The syllabus is vast but focus is on practical and analytical skills. This curriculum is most suited for the kids who have potential chances of moving in the Middle East and South Asian region due to the movement of their parents the curriculum presents an international perspective. CISCE schools are available in Dubai – Sharjah – India – Indonesia – Singapore. All schools that follow this curriculum are governed from Delhi.
International Baccalaureate Previously known as International Baccalaureate Organisation was established in the year 1968. The board offers programmes at 3 different levels for different age category. PYP or primary education programme for Kindergarten to class 5, middle year programme for class 5 to 10 and diploma programme for class 11 and 12 .
This curriculum is most suited for the kids who have potential chances of moving from one continent to another due to the movement of their parents the curriculum presents an international perspective. All schools that follow this curriculum are governed from Geneva.
Distance education in India:
Students who cannot go to colleges can complete their graduation and post graduation through distance mode. Most of the fields like Law, science, arts and commerce degree can be completed from these colleges. Some of the important university/ institutions are:
1. Indira Gandhi open university, New Delhi
2. Yashwanthrao C Maharashtra open university, Nashik
3. Sikkim Manipal open university, Gangtok
Different types of school in India
There are different kinds of school in India
Government school
Most of the government is attended by poor children. Government school provide free education up to the age of 14. To encourage children for coming to school regularly government of India provides free mid day meal to all school children along with milk. Some of the important central government schools are Kendriya Vidyalaya, Indian Army Public school and many more.
Private unaided school:
According to the survey more than 30% of Indian children enrol in private schools for completing education. It is believed and understood that the quality of education and also other extracurricular activities are much better in private school as compared to government schools. Most of the middle class family prefer to send their children to private school so that their children get better education. The ratio between the student and teacher is also much better as compared to government school.
But things are changing and even the government schools are improving and are doing their best to provide quality education even all children.
Some of the other schools include National and International schools and home schooling.
Higher education in India
The Indian Higher education has grown remarkably after India got its independence. Now Higher education in India is the third largest next to United States and China. University Grants Commission is the main governing body which also advises government and also coordinate between centre and state. There are various streams for which students can enrol for under graduation and graduation programmes.
After passing out class 12 or second PUC children can enrol for various degree programmes in arts, science and commerce and other professional courses like Law, Medicine, Engineering or Pharmacy. There are various entrance exams based on the result the student becomes eligible to join the professional courses.
Post independence the higher Education in India has improved tremendously. With the establishment of many Universities, technical institutes, Research Institutions and non professional colleges students are able to choose from wide variety of courses that are available in these universities.
The higher education in India needs a radical reform and changes for giving
quality education to the children. According to 2017 census there are around
790 universities in India which are further divided into Conventional
University, Deemed University and Institution of National importance.
Conventional University are established through the act of the Parliament,
Deemed University is an accreditation awarded to Higher education conferring
the status of University and Institute of National importance are those that has been awarded the status by
Parliament.
IGNOU or the Indira Gandhi Open University is the most important University
in distance learning in higher education in India. The Distance Education
Council which is an authority of IGNOU is coordinating State Open Universities
and institutions of correspondence courses. The HRD ministries and many
universities have also started with many online courses.
Update on coronavirus in India
Affiliate Disclosure:
If you make any purchase via a link on this site, I may receive a small commission with no added cost to you.