- Home
- History of India
- Ancient India
- Ancient Indian Art
Ancient Indian Art
Updated on 16-10-23
Ancient Indian art is a rich and diverse tradition that spans over 5,000 years. It is characterized by its deep religious symbolism, its use of bold colors and intricate patterns, and its wide range of mediums, including sculpture, painting, architecture, and textiles. The origin of the Indian art can be dated back to prehistoric settlements. Indian art has gone through various changes from ancient times to present time with the influence of culture and religions such as Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism, Sikhism and Islam.
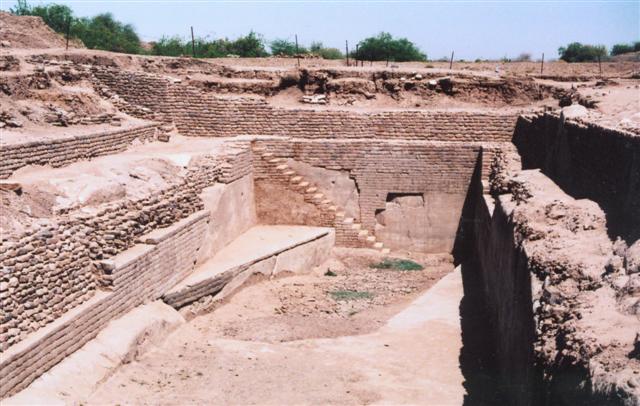
Art plays an important and prominent part in any country. Art also plays a prominent part to know about the history of that country. Art in India flourished during the Indus Valley civilisation. The artefacts which were excavated in the places where civilisation happened in India are proof to show that art was present since time immemorial. Each age had different art and culture. One can say that art in ancient India developed through all these ages and civilisations. However, it can be said that ancient art in India has undergone several transformations and improvements. It can be understood that the people of Indus Valley Civilisation were great lovers of art, paintings, sculpture and dancing .
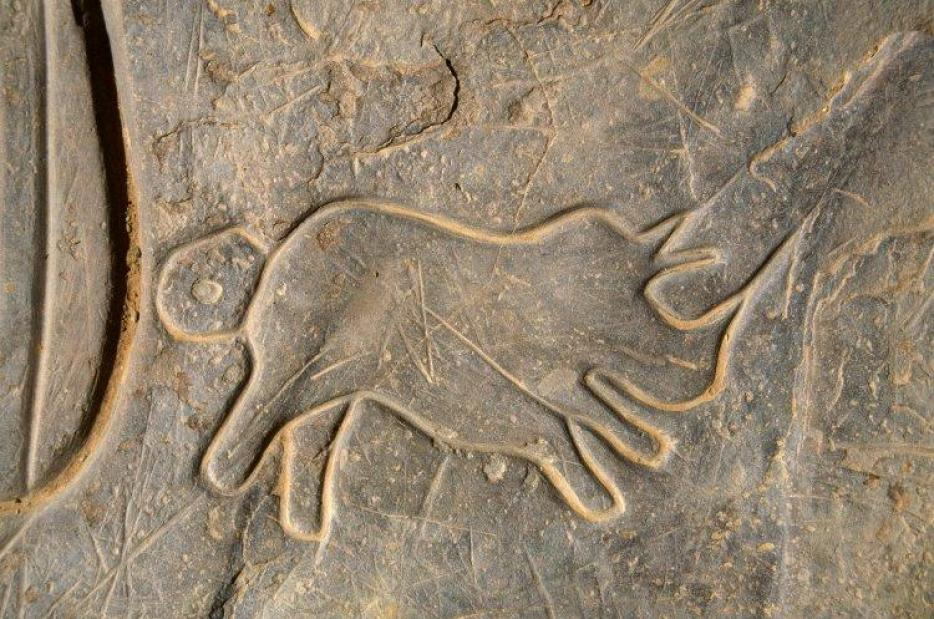
During ancient India various art forms developed like rock painting, cave painting and rock cut caves. The well developed water drainage system and development of the city during Harrapan civilisation is an indication of highly developed architecture. It also shows the skills of the people during that time. A very interesting fact of ancient Indian art is that most of the carvings or the paintings are on the rocks. The remains of these paintings or carvings are usually of animals or with some religious motifs.
Dancing Girl is a small bronze statuette from the Indus Valley Civilization (3300-1700 BC) is one of the oldest known examples of Indian sculpture. It depicts a young woman in a dynamic and graceful pose.
Rock paintings in ancient India
Rock paintings and carvings is one of the finest arts of ancient India. Some of the famous rock paintings are in Bhimbetka and in central part of India. Bhimbetka is now deemed as a UNESCO world heritage site. The paintings or the sculptures varied from one civilisation to another. Another beautiful piece of art during the Indus valley civilisation is the stone figurines of dancing girls. Some of the yoga pose figurines have also been found in Mohenjo-Daro.
However the art got a major transition and improved during the Buddhists period. Buddhists gave more importance on the development of Buddha statues which also influenced the Hindu and the Jain culture. The caves of Buddhists at Ajanta, Bhaja are marvellous. Some important stupas during Buddhists period are Sanchi stupa and Amaravati. The Hindus and Jains who got influenced with Buddhists art also developed caves Aihole, Elephanta, Badami and many more.
During the Vedic period Vedas, the earliest sacred texts of Hinduism, were composed. The Vedic period is also known for its development of arts and crafts, including pottery, metalwork, and carpentry.
The Rig Veda is a collection of hymns and prayers that were composed by the early Aryans, who migrated to India from Central Asia during the Vedic period. The Rig Veda mentions a variety of art forms, including pottery, metalworking, and woodworking. It also describes the use of music and dance in religious rituals.
Ancient Indian Art during Mauryan and Gupta Period
The art in India got further better during the Mauryan period. It was a very important period for transition from wood to stone in ancient Indian art. The Mauryan kings have built many palaces, stupas and monuments which are famous even till date. Asoka the king who took up Buddhism built many stupas and pillars during his period. Ashoka’s famous rock cut caves are found in Nagarjuna hills near Gaya. The famous lion pillar at Sarnath in which four lions are standing back to back has been adopted as Indian emblem.
The ring stone which was an artefact and a miniature sculpture was made during the Mauryan period and later followed by Sunga period. Ringstone were round in shape with a hole in the centre with beautiful carvings on it
The Gupta period is generally considered as the golden age for ancient Indian art for all religious groups.
The major surviving works of Guptas art were mostly in stone and some in metal or terracotta. The statue of Buddha at Sarnath is one of the classic examples of Gupta art during the ancient Indian period.
Buddhist Art
Ancient Buddhist art played an important role in the spread of Buddhism throughout Asia. It was used to teach the Dharma (the Buddhist teachings) and to inspire Buddhists to follow the path to enlightenment. Some of the major survivals of the Buddhists art began after the period of Mauryan.
Some of the most famous examples of ancient Buddhist art include the following:
- Ajanta Caves wall paintings: These 5th-6th century AD frescoes depict scenes from the life of the Buddha and from Buddhist mythology. They are among the finest examples of ancient Indian painting.
- Sanchi Stupa: This Buddhist monument in Madhya Pradesh, India was built in the 3rd century BC. It is one of the oldest Buddhist monuments in the world and is known for its intricate carvings.
- Amaravati Stupa: This Buddhist monument in Andhra Pradesh, India was built in the 2nd century AD. It is known for its large reliefs that depict scenes from the life of the Buddha and from Buddhist mythology.
- Gandhara sculptures: These sculptures from the Gandhara region of Pakistan were produced in the 1st-5th centuries AD. They are characterized by their Greco-Roman influence and their realistic depictions of the Buddha and other Buddhist figures.
- Mathura sculptures: These sculptures from the Mathura region of India were produced in the 1st-5th centuries AD. They are known for their expressive faces and their intricate details. Mathura region was the most important center in the development of Hindu and Jain art. the chaitya prayer hall and the monastic viharas have survived better than the free standing structures.
Indian sculpture extends from the Indus Valley, where terracotta figurines were some of the first sculptures that were formed. Throughout the Mauryan Dynasty, large stone pillars appeared at crossroads and at important sites. They often had lotus-shaped tops and figures of lions which were symbols of imperial rule. Many large stone images of gods were produced during this period, followed by smaller versions that were placed on Buddhist monuments. Stupas, burial mounds, were surrounded by ornately carved gateways featuring an array of religious symbols. More mature Indian figurative sculpture began appearing in the 2nd and 1st centuries B.C.
Earlier Mathura was the centre for the sculpture later which spread to different parts of North India. Metallurgy also made a wonderful impact during the Gupta period. The craftsmen were expert in their art of casting statues and pillars. The art got better in Gupta period and later in Mughals and during British period. It is still getting better with every generation. Art is different at different places. The art of rural and tribe people is different from urban people.
Please share your thoughts on ancient Indian art with us by clicking the link here
Update on coronavirus in India
Affiliate Disclosure:
If you make any purchase via a link on this site, I may receive a small commission with no added cost to you.