- Home
- Religions in India
- Hinduism
- Hindu Sacred Texts
Hindu Sacred Texts
Hindu Sacred Texts
Quick Links within the page
Hindu sacred texts are the voluminous literature related to different traditions and culture in Hinduism. Hinduism does not have a single sacred text like other religions. Some of the important Hindu sacred texts include Vedas, Upanishads, Purana, Itihasa, Bhagavad Gita and Agamas. Hinduism is an Indian religion followed and practised by many people world wide.
Hindu texts are divided into two categories Sruti and Smriti. Sruti is what is heard and Smriti is what is written. Sruti includes Vedas and Upanishads while Smriti includes Itihasa like Ramayana Mahabharata including Bhagavad Gita. Sruti is considered as the most authoritative and important ancient Hindu texts as it is believed that it is transmitted orally from one person to another by sages and is not written by any human beings.
In a way it can be said that sruti are something heard directly from the gods by the sages and the sages have passed it orally from one generation to another. Smritis which are less authoritative include puranas, Hindu epics, Bhashyas and Itihasa.
Sruti:
Sruti includes four Vedas or the samhithas, the Upanishads, the Brahmanas along with Aranyakas. The word sruti is a Sanskrit word which means hearing, listening or any form of communication. Sruti literature includes following texts:
The Vedas- Hindu Sacred Texts
Vedas:
Vedas are the most important ancient religious texts in Hinduism. It is composed in Vedic and Sanskrit language and is often referred to as Hindu scriptures. The Vedas existed in oral form and passed from Guru to Shishya from one generation to another. Vedas are divided into four groups 1) Rigveda 2) Yajurveda 3) Samaveda and 4) Atharvaveda. Each of these are further divided into
Aryankas-- rituals, ceremonies
Brahmanas-- performance of rituals
Samhitas ---prayers, mantras
Upanishads--- are late vedic sanskrit texts which consist of mystical and philosophical teachings of Hinduism.
The Four Vedas
Rigveda:
Rigveda is one of the oldest Vedic Sanskrit texts in Hinduism. It mainly consists of different hymns which are the prayers to Vedic Gods such as Agni (Fire), Vayu ( Air), Indra (lord of heavens) and many other gods like Sun, water. Rigveda consists of 1,028 hymns and 10,600 verses. Written in Sanskrit and dedicated to various gods, Rigveda is considered as one of the four canonical sacred texts (sruti) in Hinduism. Rigveda consists of Samhithas, Brahmanas, Aryankas and Upanishads.
Among the 1,028 hymns some of the important hymns include
- Purusha Sukta
- Hiranya-garbha Sukta
- Dhana-anna-dana Sukta
- Aksha Sukta
- Nasadiya Sukta
- Duhsvapna-nashna Sukta
- Yama-yami-samvada Sukta
Yajur Veda:
Yajurveda is the second most important veda in Hinduism. It is the collection of mantras and verses that form the part of ancient sacred literature of Vedas. It is used as a handbook by priests while performing the vedic sacrifices. It is one of the most important scriptures in Hinduism. Yajurveda is broadly divided into two groups: dark (Krishna) and white ( Shulka) Yajurveda. Dark part includes unclear verses in Yajurveda while the white part has clear and properly arranged verses. Yajurveda samhita includes 1,875 verses which are basically built on the verses of Rigveda. The four samhitas of Krishna Yajurveda include Taittiriya samhitha, Maitrayani, Kathaka and Kapishthala-katha and the white surviving samhitha include Madhyandina and Kanva.
Samaveda:
It is the third of the four Vedas which are sung in the rituals. It is known as a storehouse of knowledge of chants. It contains 1,549 verses out of which 75 are taken from Sakala Saka of Rigveda and the other 75 belong to Bashkala Sakha. The Samans of Samaveda are sung at different periods till the end of the Vedic sacrifices. The two main primary upanishads that are in Samaveda are Chandogya Upanishads and Kena Upanishad.
Some believe that the earlier part of Samaveda belongs during the Rigvedic period while the compilation dates include 1200 to 1000 BCE. Samaveda consists of two major parts in which the first part includes collection of songs and the second part has three verse books. Further the first part is divided into Gramageya and Aranyageya and the verse book is further divided into Purvarcika and Uttarcika portions. Like any other Vedas Samaveda has several layers of texts which include Samhitha and Upanishads. Samhitha being the oldest while the Upanishads is the youngest.
Atharva Veda:
Atharvaveda is the fourth veda in Hinduism and was composed between 1000-900CE It consists of 730 hymns and 6,000 mantras. These hymns and mantras are divided into 20 books. It is believed that the name is probably derived from the priest Atharvan who was a great and important religious leader.
Some scholars doubt the authenticity of this Veda due to language used and the nature of the work it suggests. Atharvaveda consists of hymns which are divided into different categories like charms, curses, hymns which are intended for healing, recovering, remedy and also prayer for peace. Book 1-7 consists of prayers for the above action. Book 8-12 consists of hymns which are part of Rigveda and also gives more speculation about Upanishads. Book 13-20 consists of magical prayers, marriage prayers, funeral prayers and also other rituals. This could be the reason as to why Atharvaveda is also called as Veda of magical formulas.
Atharvaveda consists of three Upanishads namely:
Mundaka Upanishad: It consists of 64 verses written in the form of mantra. These mantras are not used in performing any rituals but are used as teaching and for meditation purposes.
Mandukya Upanishad: It is the shortest of all the Upanishads. It explains about “OM” and asserts the existence of Atman.
Prashna Upanishad: It is also known as Prashnopanishad and is taken from Paippalada school of Atharvavedins. The Prashna Upanishad consists of six questions and each question is a chapter in itself with answers.
Upanishads
Upanishads:
Upanishads are the late Vedic texts that are the most important texts in Hinduism. Upanishad is a Sanskrit word where Upa means near and ni means down and shad means sit. So it meant a student should sit down near the teacher while learning. It is believed that sage Vyasa composed Upanishads. Even though it is not certain when Upanishads were composed however some believe that it could have been composed between 800-500 BCE. The early Upanishads were in oral form which were basically for understanding the sacrificial rites.
Upanishads are commonly referred to as Vedanta are mostly parts of the vedas. There are around 108 Upanishads out of which the oldest are considered as the Mukhya Upanishads. These Mukhya Upanishads are mostly found in the last part Brahmanas and Aryankhas and were passed from one generation to another generation orally. Mukhya Upanishads are grouped into different periods. Among these, Brihadaranyaka and Chandogya are the earliest. Each of these Upanishads are associated with one of the four Vedas. The 13 important Upanishads are
- Brhadaranyaka Upanishad
- Chandogya Upanishad
- Taittiriya Upanishad
- Aitereya Upanishad
- Kausitaki Upanishad
- Kena Upanishad
- Katha Upanishad
- Isha Upanishad
- Svetasvatara Upanishad
- Mundaka Upanishad
- Prashna Upanishad
- Maitri Upanishad
- Mandukya Upanishad
The composition of the first six Upanishads dates between 800-500 BCE and the last seven dated after 500 BCE. Upanishads are a very important source of hindu texts in Hinduism.
Smriti:
Smriti is that which is remembered. It is the written texts which are passed on from one generation to another. Smriti comprises Vedanganas, Puranas, Itihasa, Updeva, Thantra, Agamas, Upangs. It also consists of Epics like Mahabaratha and Ramayana and Dharmasutras.
Puranas
Puranas:
Puranas are the religious Hindu texts which basically consist of stories relating to Kings, sages, and Deities.It covers a wide range of topics composed mainly in sanskrit and also in other indian languages. Puranas are like encyclopedias which include wide topics like cosmology, genealogies of gods and goddess, kings, sages, temples and many others. Puranas are voluminous and diverse.
Puranas form a part of Smriti and play a very important role in understanding some of the practices and beliefs in Hinduism. The Hindu tradition recognizes 1 Maha purana, 17 Mukya Purana and 18 Upa Puranas. These are probably composed by many scholars over a period of time. But however Vyasa which is the narrator of Mahabharata is credited as the compiler of Puranas.
The Maha Puranas are classified based on the deities like Vaisnava, Agni, Vayu, sakta, Surya and Saiva. The Maha Purana is further divided into Matsya Purana, Padma Purana, Brahma Purana, Shiva Purana, Skanda Purana, Marandeya Purana, Garuda Purana, Kurma Purana, Brahmanda Purana, Vayu Purana, Bhagavata Purana, Linga Purana, Brahmavaivrata Purana.
Upapurana are also classified as Vashistha Purana, Devi, Ganesha, Parasara, Bharghava, Varuna, Nandi, Surya, Durvasa, Kapila, Bhargava and Samba Purana. Padma Purana is classified based on the truth, passion and ignorance. The three Padma Puranas are Sattva, Rajas and Tamas.
Skanda Purana is one of the largest puranas which contains 81,000 verses. Skanda is the son of lord Shiva and Uma
Puranas played a very important role in reforming Hinduism. It is basically considered as religious texts.
Bhagavad Gita
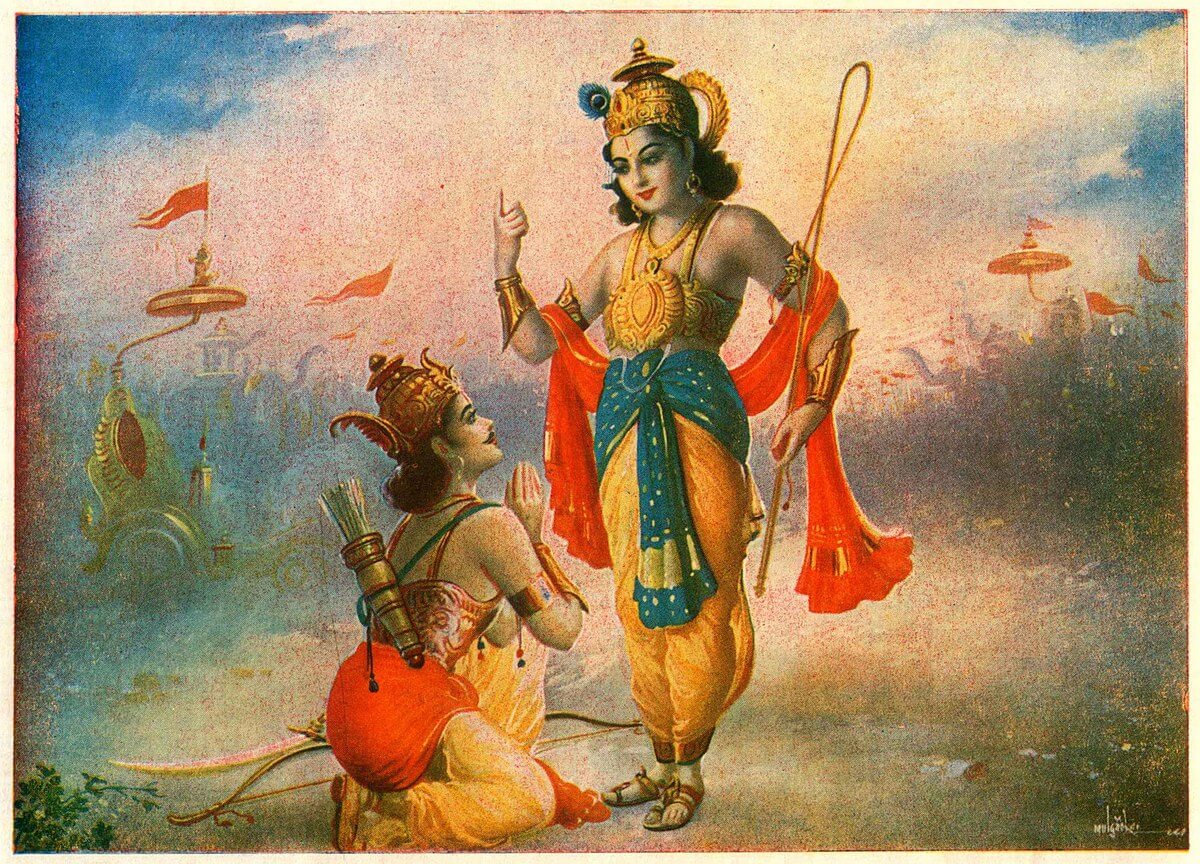 Image credit:en.wikipedia.org
Image credit:en.wikipedia.orgBhagavad Gita:
Bhagavad Gita or the song of the lord is the sixth part of Mahabharata is the world longest poem. It is the conversation between Pandava prince Arjuna and his charioteer Krishna at the battle of Kurukshetra. It is one of the most popular and sacred Hindu texts. Bhagavad gita is from chapter 23-40 in the great epic Mahabharata. Arjuna was disturbed and saddened by the death and too much violence in the battle.
On seeing so much bloodshed Arjuna wanted to withdraw from the battle. At that time Krishna asked Arjuna to fulfill his kshatriya duties and to uphold Dharma and to win over the evil. Krishna also states that the death of a person does not destroy the soul of that person. Krishna advises Arjuna that knowledge, work and devotion are all paths for salvation and most important for our life. Gita touches on many aspects of Hindu beliefs .The central theme being Dharma. Krishna convinces Arjuna how he as a warrior has to perform his duties to uphold Dharma. The text covers some of the important Hindu beliefs like jnana, bakti, karma and Raja Yoga. Bhagavad Gita in total contains 18 chapters with many verses.
Update on coronavirus in India
Affiliate Disclosure:
If you make any purchase via a link on this site, I may receive a small commission with no added cost to you.